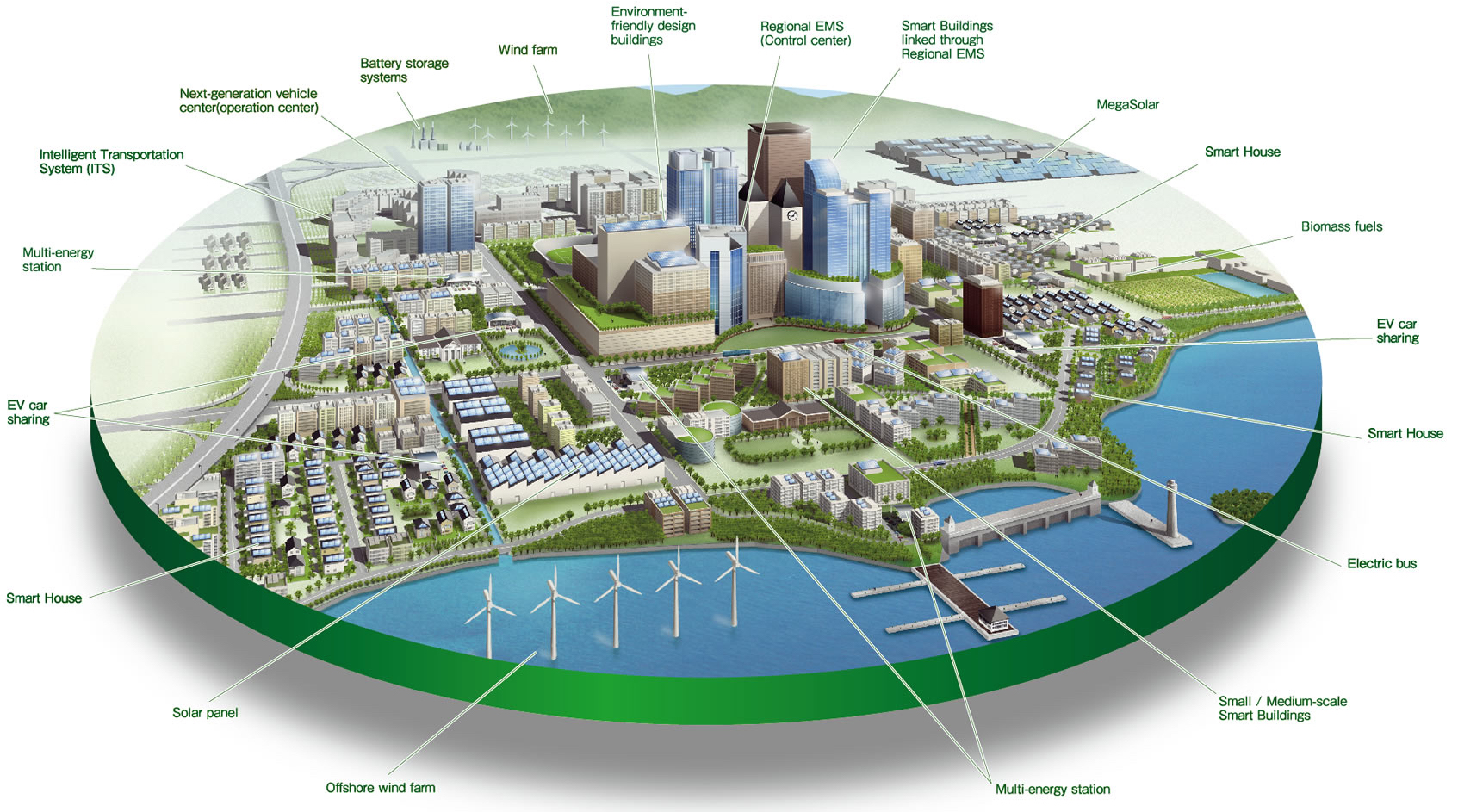
Urban planning, an ever-evolving discipline, plays a crucial role in shaping the future of our cities. As urbanization accelerates, challenges such as overpopulation, environmental impact, and strained infrastructure become more pronounced. In this article, we delve into the transformative concept of Smart Cities and the integration of sustainability practices to address the complexities of modern urban living.
Introduction
Definition of Urban Planning
Urban planning involves designing and organizing urban spaces to ensure efficient use of resources, optimal infrastructure, and a high quality of life for residents.
Evolution of Urban Planning
From ancient city layouts to the modern metropolis, urban planning has evolved to adapt to societal needs, technological advancements, and environmental concerns.
Current Challenges in Urban Planning
Overpopulation
The rapid growth of urban populations poses challenges related to housing, transportation, and resource allocation.
Environmental Impact
Urbanization often leads to environmental degradation. Addressing this impact is vital for long-term sustainability.
Infrastructure Strain
Aging infrastructure struggles to support growing populations, requiring innovative solutions for development and maintenance.
The Concept of Smart Cities
Definition and Features
Smart Cities leverage technology to enhance efficiency, connectivity, and overall urban functionality.
Integration of Technology
Incorporating IoT devices, data analytics, and interconnected systems, Smart Cities aim to create seamless and intelligent urban environments.
Sustainability in Urban Planning
Importance of Sustainable Practices
Prioritizing sustainability ensures a balance between urban development and environmental conservation.
Renewable Energy Integration
Incorporating renewable energy sources is a key component of sustainable urban planning, reducing reliance on non-renewable resources.
Benefits of Smart Cities
Efficiency and Resource Optimization
Smart Cities optimize resource utilization through data-driven decision-making, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Improved Quality of Life
Enhanced connectivity, smart infrastructure, and sustainable practices contribute to an improved quality of life for residents.
Technological Innovations in Urban Planning
IoT and Smart Infrastructure
The Internet of Things (IoT) facilitates the creation of interconnected urban systems, improving overall infrastructure efficiency.
Data Analytics for Decision-Making
Analyzing vast amounts of data enables planners to make informed decisions, enhancing the effectiveness of urban development projects.
Global Examples of Smart City Implementation
Singapore
Known for its smart mobility solutions and sustainable urban planning, Singapore serves as a model for Smart City initiatives.
Barcelona
Barcelona has embraced technology to enhance public services, from smart lighting to waste management.
Challenges in Implementing Smart City Concepts
Cost and Infrastructure Barriers
Implementing Smart City technologies requires substantial investment, posing challenges for economically strained municipalities.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Interconnected systems raise concerns about data security and the potential invasion of privacy, necessitating robust safeguards.
Community Engagement in Urban Planning
Inclusivity and Accessibility
Involving the community in the planning process ensures that diverse perspectives and needs are considered.
Public Participation
Engaging citizens fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to urban development, creating a more vibrant and connected community.
Governmental Initiatives for Smart City Development
Policies and Regulations
Governments play a pivotal role in promoting Smart City development through supportive policies and regulations.
Funding and Support
Financial backing from governments and private sectors is crucial for successful implementation and sustainability.
Balancing Technology and Human Needs
Human-Centric Design
Prioritizing human needs in the design process ensures that technology enhances rather than replaces the human experience.
Avoiding Technological Exclusion
Efforts must be made to prevent the digital divide and ensure that technological advancements benefit all segments of society.
Measuring Success in Smart Urban Planning
Key Performance Indicators
Establishing measurable KPIs helps evaluate the success of Smart City initiatives and guides future development strategies.
Long-Term Impact Assessment
Considering the long-term impact on the environment, society, and economy is essential for sustainable urban planning.
The Role of Architects and Planners in the Future
Adapting to Technological Changes
Architects and planners must embrace technological advancements to stay relevant in the evolving field of urban design.
Sustainable Design Practices
Incorporating eco-friendly and sustainable design principles is imperative for creating resilient and future-ready urban spaces.
Case Studies of Sustainable Urban Development
Curitiba, Brazil
Curitiba’s innovative public transportation system and green spaces exemplify successful sustainable urban development.
Malmo, Sweden
Malmo’s commitment to renewable energy and sustainable architecture sets an inspiring example for global cities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of urban planning lies in the integration of Smart Cities and sustainable practices. By leveraging technology, engaging communities, and adopting eco-friendly design principles, cities can become more efficient, resilient, and enjoyable places to live.
FAQs
- How do Smart Cities improve resource optimization?
- Smart Cities use data-driven decision-making to optimize resource usage, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
- What are the main challenges in implementing Smart City concepts?
- Challenges include high costs, infrastructure barriers, and concerns about privacy and security.
- Why is community engagement crucial in urban planning?
- Involving the community ensures diverse perspectives are considered, fostering a sense of ownership and commitment.
- What role do architects and planners play in the future of urban design?
- They must adapt to technological changes and prioritize sustainable design practices for resilient urban spaces.
- How can governments support Smart City development?
- Governments can provide supportive policies, regulations, and financial backing for successful implementation.